What is Chronic Kidney Disease?
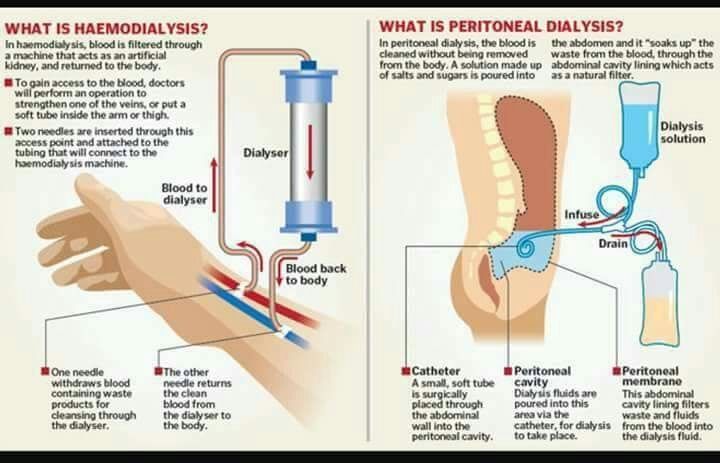
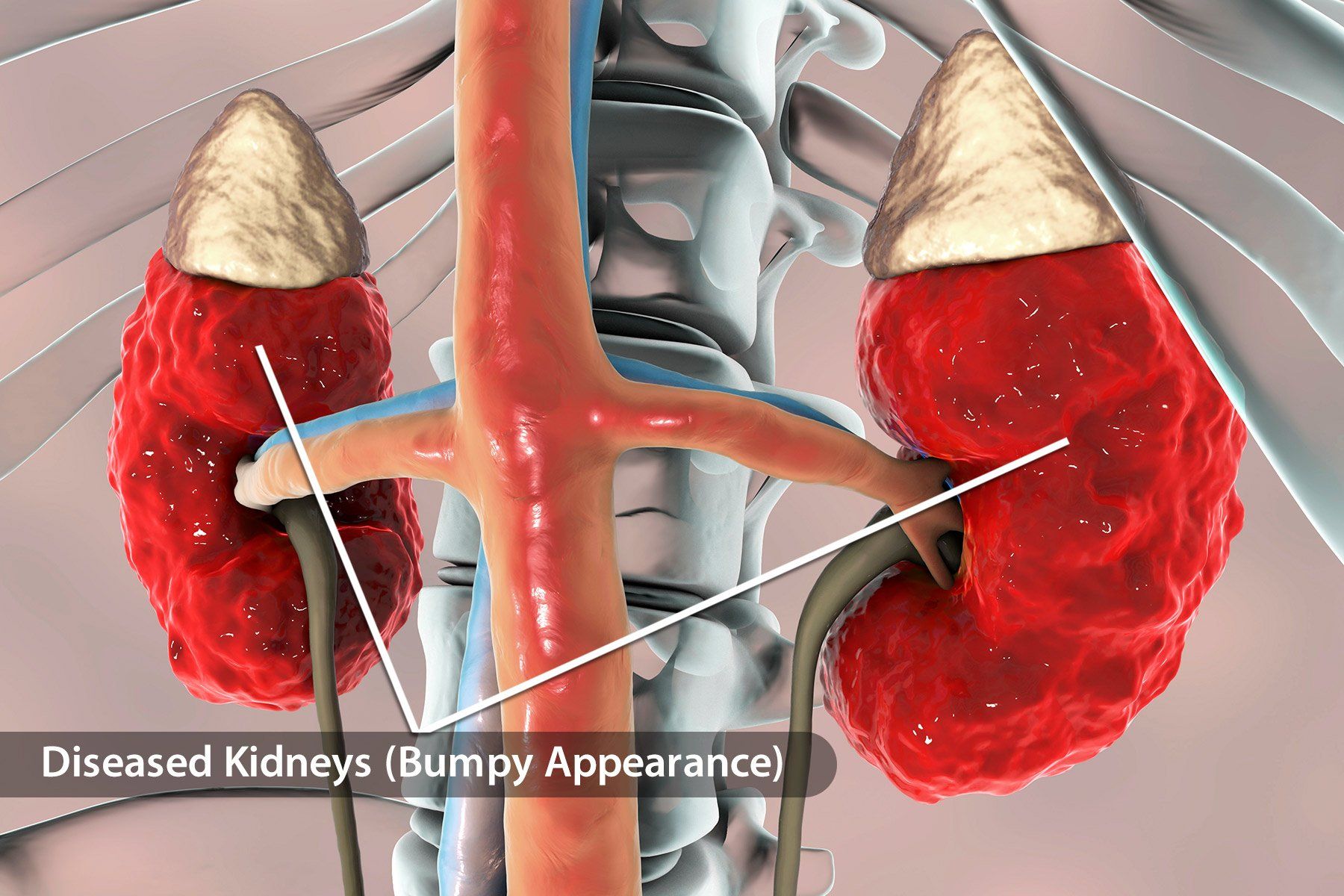
When health problems affect your kidneys, they can cause CKD. This is permanent damage that may get worse over time. If they’re so damaged that they stop working, it’s called kidney failure, or end-stage renal disease (ESRD). The treatment is usually either dialysis -- when a machine does the work your kidneys normally do, or a transplant -- when you get a new healthy kidney from a donor.
Diabetes and the Kidneys.
This leading cause of kidney failure damages the organs’ small blood vessels and filters. That makes it difficult for them to clean your blood. Your body holds on to more salt and water than it should, and there’s more waste in your system. Nerve damage caused by the disease can make urine back up and harm your kidneys through pressure or infection.
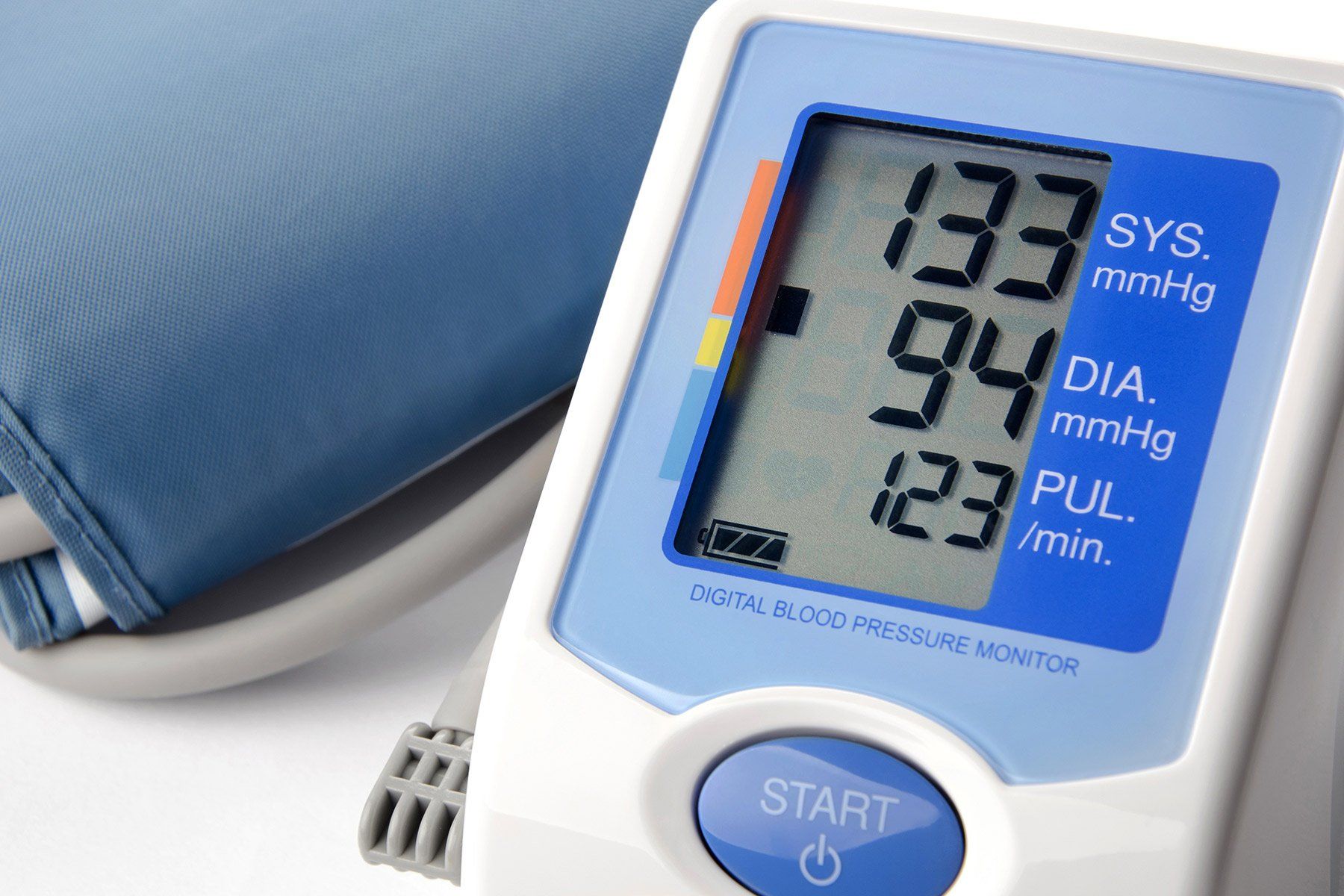
Hypertension and the Kidneys.
If the force of blood flow through your body is too high, it can stretch and scar -- and weaken -- your blood vessels, including the ones in your kidneys. This can keep them from getting rid of waste the way they should, and the extra fluid in your blood vessels can raise your blood pressure even more, leading to a dangerous cycle. It’s treated with medication and changes to things like your diet, exercise habits, and stress level